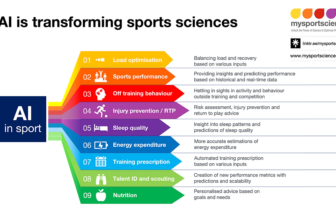
In a sequence of earlier blogs on mysportscience, the position of blood glucose was mentioned and we highlighted what insights Steady Glucose Monitoring (CGM) can present athletes now and presumably sooner or later. On this weblog, Dr Nicola Guess highlights the multifactorial nature of glucose metabolism, difficult the notion of easy causal hyperlinks between meals consumption and glycemic responses.
In earlier blogs Dr Mike Riddell and I mentioned alternatives and in addition some limitations of CGM.
There are a lot of methods during which we will have a look at CGM knowledge. We may merely have a look at a worth, or a median over 24 hours. We may have a look at the glucose variability (GV), or just depend the numbers of peaks and troughs, or maybe the time spent in a sure zone, or time spent above or under a predetermined worth. We may have a look at the slope of a peak, we may common glucose values throughout sleep or throughout train, or simply in response to 1 meal. The chances are limitless.
Like many wearables, CGM produces a number of knowledge and the interpretation of that knowledge is essential to its potential usefulness and even harmfulness. This would be the subject of this visitor weblog by Dr Nicola Guess, a Registered Dietitian with a PhD within the dietary administration of prediabetes from Imperial School London who at the moment works on the College of Oxford. On this weblog she’s going to speak about frequent misconceptions and misinterpretations. She will even talk about the modifying results of train on glucose responses and among the important variations in glucose behaviour between these people dwelling with diabetes and wholesome people.
We don't know what "regular" is but on steady glucose screens!
A standard first query from somebody utilizing CGM is: “my worth is 7.8 mmol/L [140 mg/dL], is that this good or unhealthy?” Using CGM gadgets in people (together with athletes) with out diabetes may be very latest, and whereas there's rising knowledge, we will’t outline any particular cut-offs for “good” and “unhealthy”. CGMs have been used for lots longer in kind 1 diabetes, and it’s solely prior to now couple of years that we’ve been in a position to set up among the glycaemic targets folks with kind 1 diabetes ought to intention for on a CGM. This has been attainable as a result of we now have giant datasets of individuals with kind 1 diabetes, so we will decide the glycaemic parameters from a CGM and see how they relate to the danger of issues like hypoglycaemic episodes and diabetic problems. Now we have zero helpful knowledge on CGM-derived glycaemic measures in populations with out diabetes and well being outcomes! So how can we all know for positive what glucose is “okay” on a CGM in an individual with out diabetes? We don’t, and we received’t for some time.
Now we have zero helpful knowledge on CGM-derived glycaemic measures in populations with out diabetes and well being outcomes!
The very best we will do is have a look at the CGM profiles of individuals with a “wholesome” HbA1c.
-
What’s HbA1c?
The time period HbA1c refers to glycated heamoglobin. It develops when haemoglobin, a protein inside purple blood cells that carries oxygen all through the physique, joins with glucose within the blood, changing into ‘glycated’. By measuring glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), clinicians are in a position to get an general image of what our common blood sugar ranges have been over a interval of weeks/months.
*the cut-off level for pre-diabetes can range between nations. For instance, pre-diabetes within the USA begins at 5.7%.
Observations from research investigating the CGM profiles of individuals with a “wholesome” HbA1c (beneath 5.7%), CGM-derived glucose readings sometimes present rare excursions above 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL), albeit with some variability throughout age teams. Nonetheless, caveats exist, together with potential alterations in habits throughout examine participation, which could result in underestimation of typical glucose peaks. Regardless of these challenges, knowledge from a number of research trace that occasional post-meal excursions into the Sep 11 mmol/L (162-198 mg/dL) vary could also be frequent amongst people with passable HbA1c ranges, presumably reflecting a standard facet of human glucose metabolism.
We additionally don’t know if glycaemic variability (peaks and troughs) in folks with out diabetes even matter, and in that case, how a lot. Instinctively it might sound that after all glucose going up and down loads should be a foul factor…? However we don’t even have proof of this but. Research carried out in vivo (in people) and in vitro (in cells) primarily concentrate on the kind of glucose variability you get in diabetes, the place they’re much, a lot greater (and normally sustained for longer) and the drops are decrease. Such research show the potential for top glucose variability to induce endothelial injury and different problems – however don’t precisely mirror glucose variability in people with out diabetes, the place glucose fluctuations are sometimes much less pronounced and of shorter length.
Regardless of claims relating to the advantages of stabilising blood glucose ranges, empirical proof linking glucose variability to well being outcomes, significantly in normoglycemic people, stays scant. Whereas observational research counsel weak associations between glucose fluctuations and components like starvation and vitality consumption, randomised managed trials fail to ascertain a big relationship between glycaemic peaks and dips and urge for food regulation. The complicated interaction of organic, psychological, and environmental components influencing urge for food means that glycaemic variability alone could not play a significant position in driving urge for food responses.
Glycaemic variability alone could not play a significant position in driving urge for food responses.
A transient excessive glucose doesn't imply you’ve got prediabetes or kind 2 diabetes
Impaired glucose tolerance (prediabetes) is identified by measuring an individual’s blood glucose 2 hours after a drink with 75g glucose in it. If an individual’s glucose is 7.8mmol/L (140 mg/dL) or above 2 hours after the drink, we name this impaired glucose tolerance. Nonetheless, this doesn’t imply that in case your glucose will get to 7.8mmol/L (140 mg/dL) at any time, that you’ve prediabetes. It’s fully regular on your blood glucose to get to 7.8mmol/L (140 mg/dL) 30 minutes after a drink of 75g glucose or the same carbohydrate load. The purpose is that it comes down afterwards.
The identical is true with diabetes. We diagnose diabetes when fasting glucose is 7.0 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) or extra, or when 2-hour glucose is 11.0 mmol/L (198 mg/dL) or extra. However this doesn’t imply that in case your glucose ever will get to 7.0mmol/L (126 mg/dL) or 11.0 mmol/L (198 mg/dL) that you’ve diabetes!
In actual fact, calling a glucose spike as much as e.g. 7.8mmol/L (140 mg/dL) “prediabetes” or a spike as much as 11.0 mmol/L (198 mg/dL) “diabetes” fully misunderstands the character of those circumstances. Each prediabetes and diabetes are characterised by chronically elevated glucose.
If an individual’s glucose is nonetheless at 7.8mmol/L (140 mg/dL) 120 minutes after the glucose drink it’s a sign their glucose has been a minimum of 7.8mmol/L (140 mg/dL) for the higher a part of 90 minutes. Likewise, if an individual’s fasting glucose is 7.0mmol/L (126 mg/dL) it’s in all probability been this excessive many of the evening. And if their 2-hour glucose is 11.0 mmol/L (198 mg/dL), their glucose might be elevated a minimum of this excessive many of the day.
In brief, it’s essential to discern between acute and steady glucose elevations. What distinguishes pathological from regular glucose regulation is the length of elevation. If glucose stays persistently elevated at 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL) past the anticipated postprandial interval, it may signify underlying points reminiscent of impaired beta-cell operate or insulin resistance. But, temporary excursions to this degree, adopted by a return to baseline, usually are not indicative of power hyperglycemia. Subsequently, decoding glucose readings inside a broader temporal context is important to keep away from misinterpretation and pointless concern relating to prediabetes or diabetes.
It's essential to discern between acute and steady glucose elevations.
Many components which have an effect on your glucose response to a meal don’t have anything to do with what you ate at that meal
Proponents of CGM typically tout its potential for revealing individualised responses to meals, selling a tailor-made method to food regimen primarily based on private metabolic responses. Nonetheless, this narrative oversimplifies the connection between meals consumption and glucose excursions, disregarding quite a few components that may affect postprandial glycemic responses independently of meal composition. As an illustration, the second meal impact is a well-documented phenomenon the place previous meals influence subsequent glucose responses. Moreover, physiological variations ensuing from dietary modifications, reminiscent of low-carbohydrate diets, can result in exaggerated glucose responses to subsequent carbohydrate consumption, typically inflicting undue anxiousness and dietary restrictions.
Moreover, non-dietary components like stress, sleep patterns, menstrual cycles, and train habits exert important influences on glucose homeostasis, complicating the direct interpretation of CGM knowledge in relation to dietary decisions. Stress-induced cortisol launch, sleep deprivation, and menstrual cycle phases can all alter glucose tolerance, whereas the timing and depth of bodily exercise can modulate instant glucose homeostasis and long-term insulin sensitivity. These findings problem the claims of easy causal hyperlinks between meals consumption and glycemic responses.
In case you have a look at the determine above, the glucose tour (the realm beneath the glucose curve) is way decreased (improved) after train after which reverts again to baseline after a number of days. Let’s think about you eat a bowl of oats with entire milk on day 1 – you’ll have a glucose response that appears pretty low. Now let’s think about you run out of entire milk on day 5 and have semi-skimmed milk along with your oats – you’ll get a bigger rise in glucose. You would possibly suppose that is as a result of kind of milk and resolve to have entire milk to raised management your glucose. However hopefully you’ll be able to see with this instance the change in glucose tolerance could be as a result of train you probably did – and the milk has nothing to do with it.
CGM know-how presents insights into glucose dynamics, its utility for pinpointing individualised dietary responses is proscribed by the myriad of non-dietary components affecting glycemic management.
In conclusion, whereas CGM know-how presents insights into glucose dynamics, its utility for pinpointing individualised dietary responses is proscribed by the myriad of non-dietary components affecting glycemic management.
For folks with out diabetes, glucose is a symptom of illness, not a trigger
A significant misunderstanding is the thought which you could forestall the event of kind 2 diabetes should you take steps to decrease your glucose excursions. The proper reply right here is that it depends upon what you do to decrease your glucose excursions.
Glucose that’s creeping up over time and sort 2 diabetes are each brought on by insulin resistance and failing beta-cells. So, to forestall kind 2 diabetes, you have to enhance insulin resistance and enhance the operate of the beta cells.
In different phrases, glucose is a marker for the underlying metabolic dysfunction which can ultimately result in kind 2 diabetes.
This distinction between symptom and trigger can be vital once we contemplate different illnesses reminiscent of heart problems. Insulin resistance, characterised by disruptions in intricate signaling cascades, not solely hampers glucose regulation but additionally impacts amino acid, lipid metabolism, and vascular operate, which all contribute to cardiovascular dysfunction and different well being problems.
Focusing solely on minimising glucose excursions, particularly in people with normoglycemia involved about spikes, could overlook the broader metabolic dysregulation underlying elevated glucose ranges. Such an method dangers neglecting different points of cardiovascular well being and should inadvertently exacerbate the underlying pathophysiology related to insulin resistance.
Right here you’ll be able to see the issue with consuming with the only intention of decreasing your glucose excursions – significantly in folks with normoglycaemia who’re frightened about glucose spikes. At greatest, you is perhaps consuming in such a manner that makes zero distinction to your precise threat of illness (and possibly unnecessarily depriving your self of meals you take pleasure in!) Or you possibly can even be making the underlying pathophysiology worse!
Even you probably have diabetes, glucose ranges are a tiny a part of your cardiovascular well being
It would shock you to know that even in kind 2 diabetes, medicines which considerably decrease glucose don’t essentially forestall main cardiovascular occasions like coronary heart assaults and strokes. The rationale for that is complicated (and it’s to not say decreasing glucose just isn’t a vital a part of diabetes administration) but it surely actually underscores the significance of different CVD threat components together with hypertension and excessive ldl cholesterol.
That is essential context for once we contemplate folks with (so far as we all know now) regular glucose. At the very least a 3rd of individuals within the UK have hypertension and about half have excessive ldl cholesterol. So, when it comes to the elements of metabolic and cardiovascular well being folks would profit from specializing in, it’s these. And proper now, we don’t have neat little gadgets you’ll be able to stick in your arm to measure them so tech corporations usually are not dashing to inform you how essential these are.
It's additionally value mentioning that lots of people (in all probability about 60% of the inhabitants) have elevated insulin to a level that additionally it is growing their cardiovascular threat (and different well being issues too). Insulin is a manner higher marker of metabolic well being than glucose is.
Elevated triglycerides are additionally an essential a part of cardiovascular and metabolic well being not captured with a CGM. This threat issue has added significance as a result of some issues that an individual would possibly do to decrease glucose can improve post-prandial triglycerides, reminiscent of consuming extra fats or consuming a low carbohydrate food regimen. It’s additionally value noting that GPs measure fasting triglycerides, not post-prandial triglycerides. So should you’re counting on a CGM to measure your metabolic well being, it can miss loads!
In abstract, a glucose monitor actually solely provides you a fully minuscule image of your metabolic well being. And the actions you are taking to cut back glucose (if that turns into your focus) usually are not essentially going to handle these much more essential threat components.
What can a CGM inform you and the way can glucose monitoring assist should you don't have kind 2 diabetes?
I’ve heard from some sufferers that they’ve discovered a CGM helpful for simply making them extra conscious of what they’re consuming, and so they’ve been in a position to enhance their diets and enhance their well being through the use of one. However, I’ve seen sufferers turn into extremely anxious, and actively worsen their well being (together with important rises in ldl cholesterol) through the use of a CGM.
The very best recommendation I may give is that CGMs don’t change the dietary and way of life steerage that we all know helps enhance the underlying pathophysiology of kind 2 diabetes and different illnesses. However, utilizing one would possibly show you how to stick to those modifications. As well as, we will’t know with any certainty whether or not or not frequent glucose excursions to +11mmol/L (+198 mg/dL) may trigger injury in the long term. So should you’re frightened your glucose is creeping up a bit otherwise you’re involved (after all see your physician to test), I believe it’s completely cheap to make changes to 1’s way of life right here to restrict these rises. And whether or not you wish to do that with a CGM for peace of thoughts is as much as you.
For most individuals, the next are a bunch of issues you possibly can do (you don’t must do all of them) that will be enough to decrease post-prandial glucose rises considerably:
-
Drop pounds – we’ve extremely robust proof that even modest weight lack of 3-5% physique weight lowers glucose and prevents the event of kind 2 diabetes.
-
Partaking in common bodily exercise will scale back your glucose acutely and chronically should you hold it constant.
-
Change half of your starch (rice, potatoes, bread) serving with veges.
-
Swap your starch to a legume-based pasta.
-
Have a legume aspect as an alternative of starch.
Every of those not solely acutely decrease glucose however rather more importantly, in addition they goal the underlying pathophysiology driving elevated glucose ranges – and can enhance your general metabolic and cardiometabolic well being.
Trending Merchandise