Glycogen is important for top depth train efficiency. A overview concluded that elevated glycogen focus can enhance efficiency by 2-3% and endurance capability by 15-25%. Muscle glycogen concentrations may be elevated by consuming a weight-reduction plan that’s wealthy in carbohydrate. Nevertheless, research within the 70s instructed that excessive glycogen loading protocols resulted in very excessive muscle glycogen concentrations. These protocols employed mixtures of excessive carbohydrate days, low carbohydrate days and excessive train to realize this (see a previous blog). Athletes efficiently used these carb loading protocols.
Excessive glycogen loading protocols
The protocols that have been initially used have been excessive, with glycogen depleting train 7 days earlier than competitors, 3 days of no carb consumption, 3 days of extraordinarily excessive carb consumption, no coaching for six days earlier than the race. For sure the protocol was not sensible and had a whole lot of disadvantages. However the simple finish outcome was glycogen supercompensation on the day of competitors.
There are a couple of questions although that haven’t been answered. These early research in contrast a low glycogen state of affairs with a excessive glycogen state of affairs. To the most effective of my data, research haven’t investigated regular muscle glycogen with excessive muscle glycogen or excessive versus very excessive muscle glycogen concentrations.
If we modify substrate (gasoline) availability by way of dietary manipulation (equivalent to carbohydrate loading regimens) this may have an effect on the regulation of metabolism throughout endurance train. Quite a few metabolic pathways and management factors are concerned. Most notably, rising the muscle glycogen focus will even improve the velocity with which muscle glycogen is damaged right down to pyruvate throughout train (a course of known as glycogenolysis) (1). The enzyme liable for the breakdown of glycogen (phosphorylase) is extra lively with larger glycogen concentrations.
Rising muscle glycogen focus will even improve the velocity with which muscle glycogen is damaged right down to pyruvate throughout train.
There may be one other impact. Along with glycogenolysis, muscle glycogen additionally seems to be a robust regulator of one other key enzyme in glycogen metabolism: pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH). This enzyme breaks down pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and is a price limiting step for carbohydrate oxidation. Certainly, beginning train with larger muscle glycogen leads to a higher exercise-induced improve in PDH exercise (2), and beginning with decrease glycogen reduces it.
So, are excessive glycogen loading protocols obligatory?
As I discussed, there are only a few research which have instantly addressed the variations between excessive and really excessive muscle glycogen. In a examine by Melissa Arkinstall and colleagues (3) it was noticed that glycogen utilisation was larger throughout train at 45% VO2max that was commenced with excessive glycogen versus train at 70% VO2max commenced with low glycogen focus, regardless of the upper depth.
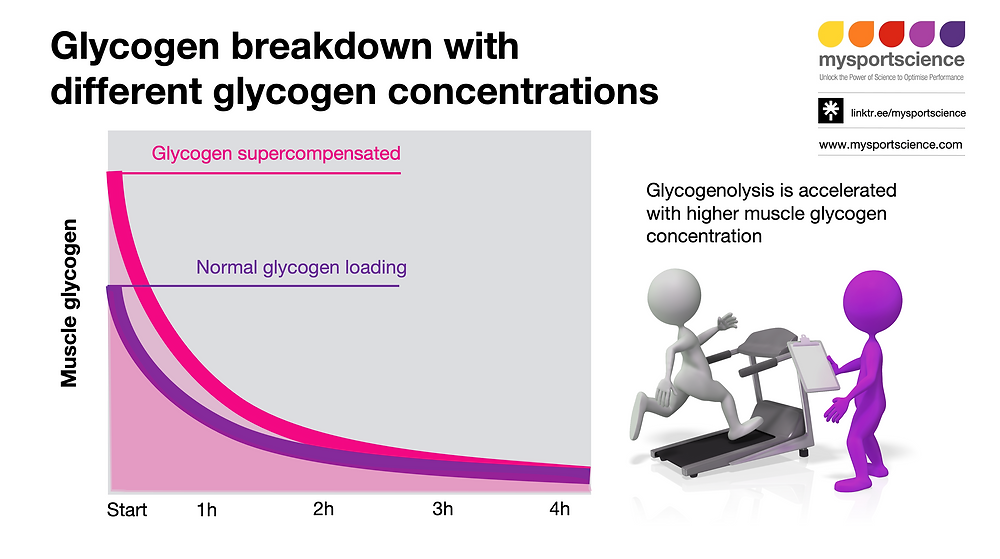
From a really sensible viewpoint. Think about operating a marathon in 3-4 hours and beginning with both excessive or very excessive muscle glycogen concentrations. The infographic is a theoretical modelling of what would occur with muscle glycogen concentrations. The primary hour there can be a distinction within the focus however in each situations there can be ample glycogen to run at excessive tempo. After 2 hours in each situations the glycogen concentrations will develop into depleted and the distinction between situations is now minimal. In direction of the tip of the marathon glycogen concentrations are in all probability comparable. So is there actually a bonus of a extra excessive carb loading protocol?
Conclusions
One might argue that there nonetheless could be a small distinction as a result of within the first hour operating can be extra economical. The upper carbohydrate oxidation within the first hour would require much less oxygen. The counterargument can be that oxygen uptake isn’t a limiting issue on this situation. So till somebody rigorously conducts the examine the place excessive glycogen and really excessive glycogen are in contrast, we could by no means know, however it appears that evidently any benefits of maximum carb loading could be outweighed by the disadvantages of such regimens within the week main as much as a race.
References
-
Hargreaves M., McConell G., Proletto J. Affect of muscle glycogen on glycogenolysis and glucose uptake throughout train in people. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995;78:288–292
-
Kiilerich Ok., Gudmundsson M., Birk J.B., Lundby C., Taudorf S., Plomgard P., Saltin B., Pedersen P.A., Wojtaszewski J.F.P., Pilegaard H. Low muscle glycogen and elevated plasma free fatty acid modify however don’t forestall exercise-induced PDH activation in human skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 2010;59:26–32
-
Arkinstall M.J., Bruce C.R., Clark S.A., Rickards C.A., Burke L.M., Hawley J.A. Regulation of gasoline metabolism by pre-exercise muscle glycogen content material and train depth. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004;97:2275–2283
Trending Merchandise